40 plastids diagram with labels
Plastids - Definition, Types, Main Structure and Function Studies have also shown the plastid to be polarized and ranging from 5 to 10 micrometers in width depending on the plant. Like the other plastids, chloroplasts have a double membrane envelope consisting of the outer and inner membrane (phospholipid layers). The space within the double membranes is covered with an aqueous matrix known as stroma. Simple Plant Cell Diagram Without Labels Images Result The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch, large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell turgor pressure.. Learning the names of some plant cell parts can be challenging, but this quiz.
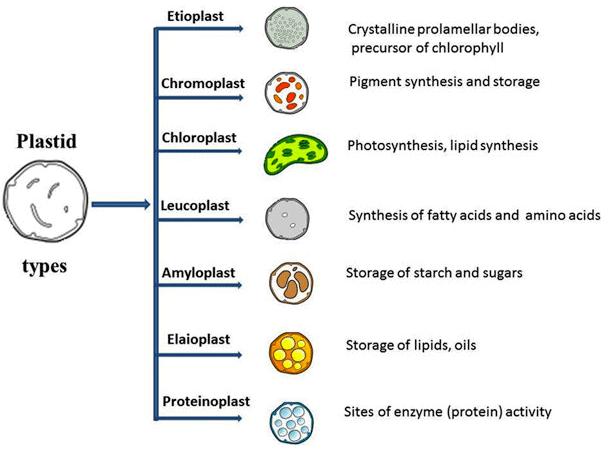
Study Notes on Genetics of Plastids (With Diagram) The below mentioned article provides a study note on Genetics of Plastids. In the cytoplasm of the plant cells are found many small cytoplasmic bodies, called plastids. These plastids are of several types, such as, chloroplast, leucoplast, chromoplast and so on. Plastids arise from smaller particles, the proplastids, found in the egg cytoplasm.
Plastids diagram with labels
Plant Cell Diagram Plastids Structure : Functions and Diagram Friday, February 12th 2021. | Diagram Plant Cell Diagram Plastids. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cells of autotrophic eukaryotes. It is the second largest organelle of the cell which is bounded by a double unit membrane and may be colored or colorless. Plastids In Plant Cell Diagram Structure : Functions and Diagram Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, while A. Mayer and Schimper first used the term plastid. Most cultured cells that are relatively large compared to other plant cells have very long and abundant stromules that extend to the cell periphery. A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles A major component of plants that are starchy in nature, the amyloplasts are organelles that store starch. They are classified as plastids, and are also known as starch grains. They are responsible for the conversion of starch into sugar, that gives energy to the starchy plants and tubers. Function: S ynthesizes and stores starch granules.
Plastids diagram with labels. Integration of plastids with their hosts: Lessons learned from ... The endosymbiotic acquisition and secondary loss of each individual plastid lineage, the loss of nonphotosynthesis genes from the peridinin plastid lineage, and the origins of minicircles, poly(U) tail addition, and transcript editing in peridinin and fucoxanthin plastids are labeled on the diagram. Plastids: Definition, Diagram, Types, and Plastid Function ... Mar 04, 2022 · Types of Plastids and Functions of Plastids Plastids are further divided into 3 types that have different functions and some have biological pigments as well. 1. Leucoplasts 2. Chromoplasts 3. Chloroplasts Leucoplasts These colourless Plastids possess internal lamellae and do not contain photosynthetic and grana pigments. Plant Cell Diagram Labeled Quizlet : Animal Cell Diagram Labelling ... In your answer, be sure to: Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com. Select one cell structure labeled in the diagram and write its number in the space below. There are various cell organelles, out if which, some are common in most types of cells like cell membranes, nucleus, and cytoplasm. Plastid and its various types with their respective organelle ... Download scientific diagram | Plastid and its various types with their ... the single-label, single & dual-label combined, and dual-label proteins, ...
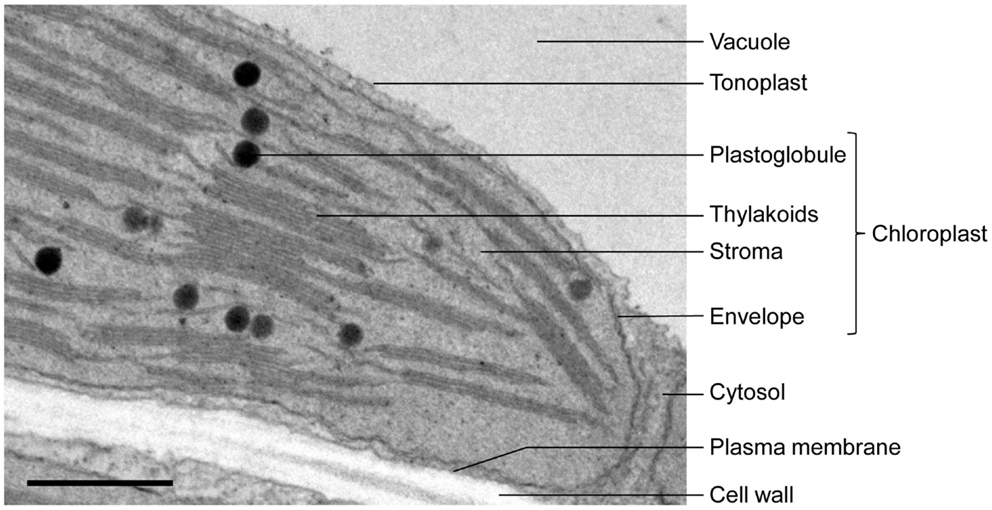
Plastid - Wikipedia There is an illustration of stages depicted by the diagram mentioned above in which it is shown inter-conversion of Plastids In 1977 J.M Whatley proposed a plastid development cycle which said that plastid development is not always unidirectional but is a cyclic process several times. Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Structure of Plastids Chloroplasts may be spherical, ovoid, or discoid in higher plants and stellate, cup-shaped, or spiral as in some algae. They are usually 4-6 µm in diameter and 20 to 40 in number in each cell of higher plants, evenly distributed throughout the cytoplasm. Cell Organelles- Definition, Structure, Functions, Diagram Plastids Ribosomes Storage granules Vacuole Vesicles Cell membrane (Plasma membrane/ Plasmalemma) A plasma membrane is composed of lipids and proteins where the composition might fluctuate based on fluidity, external environment, and the different stages of development of the cell. Structure of Cell Membrane Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma and lamella can be clearly marked out. Chloroplast Diagram representing Chloroplast Structure
Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure Animal Cells Organelles and Functions. A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. The control center of the cell. Nucleus contains majority of cell's the DNA. Popularly known as the "Powerhouse". Breaks down food to produce energy in the form of ATP. Diversity of Plastid Types and Their Interconversions - Frontiers by H Choi · 2021 · Cited by 6 — Plastids are pivotal subcellular organelles that have evolved to perform ... Schematic diagram of the plastid transition regulations. Plastids - Leucoplasts, Chromoplasts and Chloroplasts. These are colourless plastids found in the storage organs. They are found large numbers in the cells of fruits, seeds, tubers etc. They are variously shaped, viz., oval, rod like, or filamentous. They lack grana and photosynthetic pigments. They are of three types: Amyloplasts, Aleuronoplast (Proteinoplast) and Elaioplast or oleosomes. Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure The cell wall is made of cellulose and lignin, which are strong and tough compounds. Plant Cells Labelled Plastids and Chloroplasts Plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Plant cells have plastids, which animal cells don't. Plastids are organelles used to make and store needed compounds. Chloroplasts are the most important of plastids.
Plastids: Everything You Need to Know and More Plastids are a diverse group of double-membrane bound organelles found in most plants and algae. They may also be found in ferns, moss, parasitic worms and marine mollusks. Apart from photosynthesis, these organelles also assist in food storage and synthesis of compounds such as lipids, amino acids and carbohydrates.
Plant Cell Diagram - Diagrammatic representation of a generalized plant ... Label the organelles in the diagram below. Part 1 is the cell wall. Animal cells come in all kinds of shapes and sizes, with their size ranging from a few millimeters to micrometers. Older students can be challenged to identify and label the animal cell parts. A schematic diagram showing a simple layering process.
Divine Label Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Structure of Plastids Chloroplasts may be spherical, ovoid, or discoid in higher plants and stellate, cup-shaped, or spiral as in some algae. They are usually 4-6 µm in diameter and 20 to 40 in number in each cell of higher plants, e
Plastids - Types and Structure - VEDANTU On the foundation of the presence or absence of pigments, and the phase of development, plastids have been classified into proplastids, leucoplasts, and chromoplasts. Proplastids Minor vesicular structures present in meristematic cells are called proplastids. They are colorless and immature.
Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The chloroplasts are the cell organelles which consist of these pigments. The 3 types of pigments present in plants are chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins. Chlorophyll imparts the green color to plants. Plastids are membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles that can be found in the cells of plants and algae.
Plastids - Different types of Plastids and their functions in ... There are different types of plastids with their specialized functions. Among them, a few are mainly classified based on the presence or absence of the Biological pigments and their stages of development. Chloroplasts Chromoplasts Gerontoplasts Leucoplasts Chloroplasts
Plastids: Types, Structure and Function (With Diagram) Plastids may be coloured or colourless and are of three types. The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids principally serving the purpose of storage. On the basis of nature of storage compound, leucoplastids are amyloplasts (starch), elaioplasts (oil) or aleuroplasts (protein). The green plastids or chloroplastids are needed for photosynthesis.
Types of Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Functions, Labeled Diagram the most common plastid known as chloroplasts is made up of chlorophyll, a green pigment responsible for capturing light energy and converting it to chemical energy that is used by plants in photosynthesis. other plastids include amyloplast for storage of starch, elaioplast, for storage of fats, and chromoplasts for synthesis and storage of …
Plant Cell Diagram With Labeled Parts Images Result Diagram showing anatomy of plant cell 419163 Vector Art at Width: 5389, Height: 4082, Filetype: jpg, Check Details. Draw plant cell using suitable colours and label it :. They are mostly present in the leaf epidermis, stem pith, root and fruit pulp. Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com.
Animal Cell Structure Labeled Mastering Biology - Pin by Nicole ... Cellular structures and components can be labeled with a variety of fluorescent dyes that can be visualized. Plant cell diagram labeled diagram of a plant cell with. Identify two functions of plastids in plant cells. Under a microscope, most animal and plant. The largest organelle within the cell.
draw a well labelled diagram of a plastid? where is it found ... Sep 12, 2017 — Plastids are present only in plant cells. There are two types of plastids- chromoplasts and leucoplasts. Chromoplasts are coloured plastids ...
Plant Cell: Diagram, Types and Functions - Embibe Exams Plastids in Plant Cell. They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA. They are necessary to store starch, to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used in the synthesis of many molecules, which form the building blocks of the cell. Based on the type of pigment, they are of Plastids are of three types: a.
Plastids: Definition, Structure, Types & Functions - Study.com Oct 10, 2021 — Plastids are double membrane-bound organelles found inside plants and some algae, which are primarily responsible for activities related to ...
A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and Functions of its Organelles A major component of plants that are starchy in nature, the amyloplasts are organelles that store starch. They are classified as plastids, and are also known as starch grains. They are responsible for the conversion of starch into sugar, that gives energy to the starchy plants and tubers. Function: S ynthesizes and stores starch granules.
Plastids In Plant Cell Diagram Structure : Functions and Diagram Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram They were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, while A. Mayer and Schimper first used the term plastid. Most cultured cells that are relatively large compared to other plant cells have very long and abundant stromules that extend to the cell periphery.
Plant Cell Diagram Plastids Structure : Functions and Diagram Friday, February 12th 2021. | Diagram Plant Cell Diagram Plastids. Plastids are the site of manufacture and storage of important chemical compounds used by the cells of autotrophic eukaryotes. It is the second largest organelle of the cell which is bounded by a double unit membrane and may be colored or colorless.











Post a Comment for "40 plastids diagram with labels"