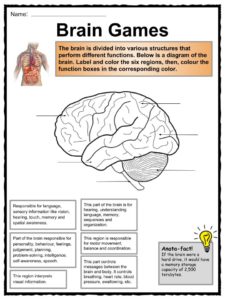
42 brain labels and functions
Parts of the brain: Learn with diagrams and quizzes - Kenhub Labeled brain diagram First up, have a look at the labeled brain structures on the image below. Try to memorize the name and location of each structure, then proceed to test yourself with the blank brain diagram provided below. Labeled diagram showing the main parts of the brain Blank brain diagram (free download!) Positions and Functions of the Four Brain Lobes - MD-Health.com Brain Lobes and their Functions The brain is divided into four sections, known as lobes (as shown in the image). The frontal lobe, occipital lobe, parietal lobe, and temporal lobe have different locations and functions that support the responses and actions of the human body. Let's start by identifying where each lobe is positioned in the brain.
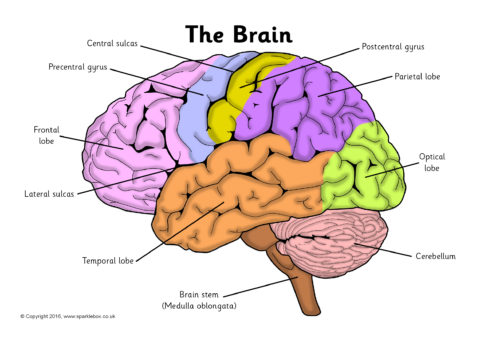
Lobes of the brain - Queensland Brain Institute Bumps and grooves of the brain In humans, the lobes of the brain are divided by a number of bumps and grooves. These are known as gyri (bumps) and sulci (groves or fissures). The folding of the brain, and the resulting gyri and sulci, increases its surface area and enables more cerebral cortex matter to fit inside the skull.

Brain labels and functions
Diagram of the Brain and its Functions - Bodytomy Functions The frontal lobe is involved with the main executive functions of the brain, which include: Judgment, that is, the ability to recognize future consequences resulting from ongoing actions. This activity mostly occurs in the pre-frontal area. Analytical and critical reasoning. Cognition and memory is mostly concentrated in the frontal lobe. Anatomy of the Brain: Structures and Their Function Brain Divisions . The forebrain is the division of the brain that is responsible for a variety of functions including receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function. There are two major divisions of forebrain: the diencephalon and the telencephalon. The diencephalon contains structures such as the ... Brain Anatomy and How the Brain Works - Hopkins Medicine Functions of the medulla regulate many bodily activities, including heart rhythm, breathing, blood flow, and oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. The medulla produces reflexive activities such as sneezing, vomiting, coughing and swallowing. The spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull.
Brain labels and functions. Lobes of the brain: Structure and function | Kenhub The brain is composed of the cerebrum, cerebellum and brainstem. The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, and is divided into a left and right hemisphere. Although the cerebrum appears to be a uniform structure, it can actually be broken down into separate regions based on their embryological origins, structure and function. Brain - Label Flashcards | Quizlet Brain - Label STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Grace_Tierney Terms in this set (27) Hypothalamus 1 Optic chiasma 2 Pituitary gland 3 Pons 4 Medulla oblongata 5 Cerebral hemisphere 6 Corpus callosum 7 Thalamus 9 Pineal gland 10 Midbrain 11 Frontal lobe 1 Parietal lobe 5 Occipital lobe 8 Temporal lobe 9 Cerebellum Nervous System - Label the Brain This brain part controls balance, movement, and coordination. (11) This brain part controls involuntary actions such as breathing, heartbeats, and digestion. (12) This part of the nervous system moves messages between the brain and the body. (13) This part of the cerebrum interprets and sorts information from the senses. (14) Brain (Human Anatomy): Picture, Function, Parts, Conditions, and More • The cerebellum is at the base and the back of the brain. The cerebellum is responsible for coordination and balance. The brain is also divided into several lobes: • The frontal lobes are...
The Brain Labeling and Functions Flashcards | Quizlet frontal lobe function reasoning and motor skills parietal lobe function processing sensory information occipital lobe function visual stimuli temporal lobe function interpreting sound and language memory cerebellum function posture and balance/ motor coordination brain stem function basic vital life functions (breathing, heart beat, blood pressure) › pmc › articlesHow does the brain solve visual object recognition? - PMC Feb 09, 2012 · Introduction. Recognizing the words on this page, a coffee cup on your desk, or the person who just entered the room all seem so easy. The apparent ease of our visual recognition abilities belies the computational magnitude of this feat: we effortlessly detect and classify objects from among tens of thousands of possibilities (Biederman, 1987) and we do so within a fraction of a second (Potter ... Anatomy of the Brain - Simply Psychology The main functions of these lobes include understanding, language, memory acquisition, face recognition, object recognition, perception, and processing auditory information. There is a temporal lobe in both the left and right hemispheres. Functions of a Brain - Making Headway Center Functions of a Brain Frontal Lobe Functions Attention and concentration Self-monitoring Organization Speaking (expressive language) • Motor planning and initiation Awareness of abilities and limitations Personality Mental flexibility Inhibition of behavior Emotions Problem solving Planning and anticipation Judgment Parietal Lobe Sense of touch
Parts of the Human Brain | Anatomy & Function - Study.com A human brain is composed of several parts, each with its own function. The parts of the brain include the cerebrum, the cerebellum, the brain stem, and the pituitary gland. The brain structure is ... learning-center.homesciencetools.com › articleSheep Brain Dissection Project Guide | HST Learning Center Sheep Brain Dissection: Internal Anatomy. Place the brain with the curved top side of the cerebrum facing up. Use a scalpel (or sharp, thin knife) to slice through the brain along the center line, starting at the cerebrum and going down through the cerebellum, spinal cord, medulla, and pons. Separate the two halves of the brain and lay them ... Labeled Diagrams of the Human Brain You'll Want to Copy Now Labeled Diagrams of the Human Brain Central Core The central core consists of the thalamus, pons, cerebellum, reticular formation and medulla. These five regions are the central areas that regulate breathing, pulse, arousal, balance, sleep and early stages of processing sensory information. Major Structures and Functions of the Brain - NCBI Bookshelf Nerves in the midbrain also control some movements of the eyeball, pupil, and lens and reflexes of the eyes, head, and trunk. Thalamus And Hypothalamus Deep in the core area of the brain, just above the top of the brainstem, are structures that have a great deal to do with perception, movement, and the body's vital functions.
The Human Brain: Anatomy and Function - Visible Body Rotate this 3D model to see the four major regions of the brain: the cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, and brainstem. The brain directs our body's internal functions. It also integrates sensory impulses and information to form perceptions, thoughts, and memories. The brain gives us self-awareness and the ability to speak and move in the world.
Functions of the Brain - Brain Injury Association of America The brain is made up of many parts, each with a specific and important function. It controls our ability to balance, walk, talk, and eat. It coordinates and regulates our breathing, blood circulation, and heart rate. It is responsible for our ability to speak, to process and remember information, make decisions, and feel emotions.
Diagram Of Brain with their Labelings and Detailed Explanation The parietal lobe is found at the upper back of our brain. This lobe functions by controlling all our complex behaviours, including senses of vision, the sense of touch, spatial orientation and body awareness. It manages body position, movements, the perception of stimuli, orientation, handwriting and visuospatial processing. The Occipital Lobe
› eeg-guideThe Introductory Guide to EEG (Electroencephalography) - EMOTIV EEG can measure cognitive functions — such as attention and distraction, stress and cognitive load (the brain’s total capacity for mental activity imposed on working memory at any moment). These findings can reveal valuable insights into how the brain responds to daily life events.
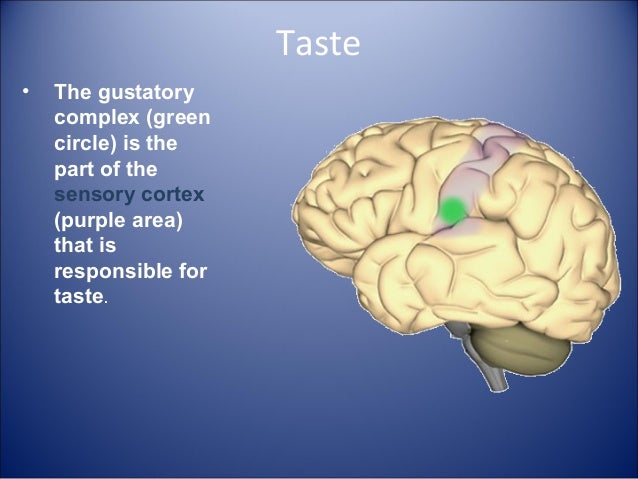
Brain Regions and Functions | Ask A Biologist The brain is a very busy organ. It is the control center for the body. It runs your organs such as your heart and lungs. It is also busy working with other parts of your body. All of your senses - sight, smell, hearing, touch, and taste - depend on your brain. Tasting food with the sensors on your tongue is only possible if the signals from ...
DOC Brain Anatomy Function Cheat Sheet Controls/regulates heartbeat and breathing To and from brain Reticular Formation Helps control arousal, responds to change in monotony Thalamus Relays sensory information, switchboard between sensory neurons and higher brain regions Deals with sight, hearing, touch, taste. Transmits replies from higher brain to cerebellum and medullam
Labeled Brain Model Diagram | Science Trends The cerebrum is the largest and most complex portion of the human brain. The cerebrum's function is to control our actions and thoughts, either conscious or unconscious, and responses to stimuli. The cerebrum itself is typically divided into four different lobes: the temporal lobe, the parietal lobe, the occipital lobe, and the frontal lobe.
› news › mind_brainMind & Brain News -- ScienceDaily Jun 08, 2022 · Psychology news from leading research institutes around the world. Research on relationships, new treatments for mental health conditions, and more. Updated daily.
› brain-controlled-technologyBrain Controlled Technology using Emotiv's Algorithms - EMOTIV Brain control can replace traditional input devices like keyboards, enhance interactive experiences and provide new ways for the disabled to engage with their surroundings. Integrate Emotions With EMOTIV’s Performance Metrics, an individual’s real-time cognitive and emotional state can be used to passively modulate an application.
Label The Brain - Mr. Barth's Class Label The Brain. The following websites are to help you learn and remember the parts of the brain and their locations. Please go through each of websites and become familiar with each of the parts of the brain. I would advise you to repeat each of them a few times until you have the locations memorized. Click on the link to the left to review ...
labeling.ucsd.edu › tutorial › labelsSCCN: Independent Component Labeling The power spectrum also suggests a brain source because of the peak at 10 Hz. This is continuous data, so there is no ERP (although there needn't always be one either). This component is also well fit by a single dipole located in the brain, but is deeper in the brain than would be expected (visible in the dipole plot).
Brain - Human Brain Diagrams and Detailed Information Many of the most basic survival functions of the brain are controlled by the brainstem. The brainstem is made of three regions: the medulla oblongata, the pons, and the midbrain. A net-like structure of mixed gray and white matter known as the reticular formation is found in all three regions of the brainstem. The reticular formation controls ...
Difference Between Stem Cells and Differentiated Cells | Definition, Morphology, Types, Function ...
Structure, Diagram, Parts Of Human Brain - BYJU'S The human brain controls nearly every aspect of the human body ranging from physiological functions to cognitive abilities. It functions by receiving and sending signals via neurons to different parts of the body. The human brain, just like most other mammals, has the same basic structure, but it is better developed than any other mammalian brain.
Brain: Anatomy, Pictures, Functions, and Conditions The brain can also be affected by a number of conditions and by damage. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, there are more than 600 types of neurological diseases. Some conditions that can affect the brain and its function include: Brain tumors; Cerebrovascular diseases such as stroke and vascular dementia








Post a Comment for "42 brain labels and functions"